Define Free Radicals In Chemistry
Most molecules contain even numbers of electrons and the covalent chemical bonds holding the atoms together within a molecule normally consist of pairs of electrons jointly shared by. Radicals are usually formed when a single covalent bond breaks to leave an unpaired electron on each of the two species created by the bond breaking.
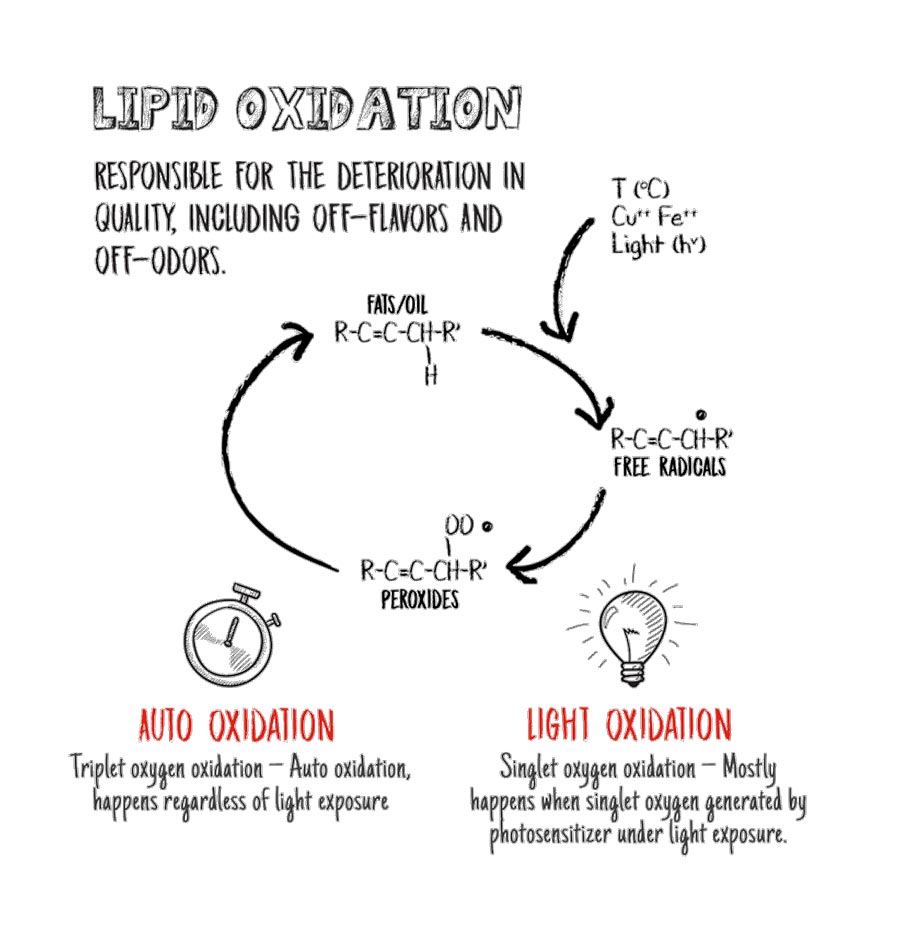
Effects Of Oxidation On Food Shelf Life Extension Expert
One that is produced in the body by natural biological processes or introduced from an outside source such as tobacco smoke toxins or pollutants and that can damage cells proteins and DNA by altering their chemical structure.
Define free radicals in chemistry. A radical in its usually transient uncombined state. The molecules that have unpaired electrons are called free radicals and such radicals can be easily mixed with their respective components without getting affected by the outside atmosphere. Radical chemistry In chemistry radicals often referred to as free radicals are atomic or molecular species with unpaired electrons on an otherwise open shell configuration.
Instead a radical specifically a free radical is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron. Free radicals are capable of starting rapid chain-reactions that destabilize the ions in other nearby molecules generating more free radicals. Free radicals are usually highly reactive and unstable.
An atom or molecule that bears an unpaired electron and is extremely reactive capable of engaging in rapid chain reactions that destabilize other molecules and generate many more free radicals. The first organic free radical identified was triphenylmethyl radical. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselvesa process that can cause damage to DNA and other parts of human cells.
An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the. This species was discovered by Moses. An atom or atom group carrying an unpaired electron and no charge.
Human beings contain 1000020000 free radicals which attack each and individual cell of our body. Chlorine gas can be broken down by ultraviolet light to form atomic chlorine radicals. Depiction in chemical reactions.
Free radical definition is - an especially reactive atom or group of atoms that has one or more unpaired electrons. In the body deactivated by antioxidants uric acid and certain enzyme activities. Unpaired electron indicate odd number of valence shell electrons For example.
Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. In Chemistry a free radical is an atom or a molecule free in its space and independent in its nature. The free radical nitric oxide NO plays an important role in vasodilation.
Free radicals may be involved as short-lived highly active intermediates in various reactions in living tissue notably in photosynthesis. Free radicals are uncharged very reactive and short-lived molecules. The most common definition of free radicals is molecules or molecular fragments containing one or more unpaired electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals 3.
They are produced by homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond see chemical bond chemical bond. The formation of radicals may. In biological systems free radicals are deactivated by anti-oxidants uric acid and certain enzyme activities.
An atom or group of atoms that has at least one unpaired electron and is therefore unstable and highly reactive. What are free radicals. Radical also called Free Radical in chemistry molecule that contains at least one unpaired electron.
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. In animal tissues free radicals can damage cells and are believed to accelerate the progression of cancer cardiovascular disease and age-related diseases. In the past such species were often called free radicals.
Free Radicals History. A radical is a chemical speciesthat contains an unpaired electron. Free radical Definition Chemical specie atommolecule having unpaired valence shell electron.
Hydrogen atom having unpaired valence electron 1e-. This is called homolysis. Free radical in chemistry a molecule or atom that contains an unpaired electron but is neither positively nor negatively charged.
Formation Of Free Radicals In The Body
Substances and energy sources from the environment can add to or accelerate the production of free radicals within the body. The major sources of free radicals include.

Free Radicals In The Physiological Control Of Cell Function Physiological Reviews
Learn about what causes them to form and how you can protect yourself from them.
Formation of free radicals in the body. This threat is reduced in the healthy state where because of the fine iron metabolism regulation there is never appreciable concentration of free iron. The liver produces free radicals as it breaks down compounds and removes them. Substances and energy sources from the environment can add to or accelerate the production of free radicals within the body.
The bodys cells produce free radicals during normal metabolic processes. Free radicals are thought to be responsible for age-related changes in appearance such as wrinkles and gray hair. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.
When the amount of free radicals exceeds the bodys ability to eliminate or neutralize them an oxidative imbalance results. Substances and energy sources from the environment can add to or accelerate the production of free radicals within the body. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive.
Free Radicals in the Body As previously mentioned our bodies create these unstable molecules through normal essential metabolic processes. 5 Ordinary body functions such as breathing and digestion. For instance when your body uses oxygen it creates free radicals as a byproduct and results in oxidative stress.
However iron is also biochemically dangerous. Free radicals can cause permanent damage to our bodies. Understanding free radicals requires a basic knowledge of chemistry.
In general the body is able to maintain a. The body creates free radicals through the normal processes of metabolism. It can damage tissues by catalyzing the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to free-radical ions that attack cellular membranes protein and DNA.
The free radical theory of aging FRTA states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. When the amount of free radicals exceeds the bodys ability to eliminate or neutralize them an oxidative imbalance occurs. The free radicals both the reactive oxygen species ROS and reactive nitrogen species RNS are derived from both endogenous sources mitochondria peroxisomes endoplasmic reticulum phagocytic.
However cells also produce antioxidants that neutralize these free radicals. The body creates free radicals through the normal processes of metabolism. Free radicals are generated due to oxidation and when toxins are broken down in the body.
Free radicals are highly reactive and unstable molecules that are produced in the body naturally as a byproduct of metabolism oxidation or by exposure to toxins in the environment such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet light. The body creates free radicals through the normal processes of metabolism. Though there are many types of free radicals that can be formed the most common in aerobic oxygen breathing organisms are oxygen free radical.
Free radicals are the result of stress diet smoking exercise alcohol inflammation drugs or even exposure to air pollutants and sunlight. When the amount of free radicals exceeds the bodys ability to eliminate or neutralize them an oxidative imbalance results.
